South Korea adopts mandatory registration of overseas food factories. However, South Korea requires only the basic information about the facility for registration. The continuous increase in import amounts and the high incidence of nonconformities of certain items have necessitated a change in the management system for imported foods. Therefore, as revealed by the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (MFDS) on February 28, 2023, a new differential registration scheme1 (해외제조업소 차등 등록제) for foreign food facilities manufacturing foods with potential risks was newly introduced. The importers are required to submit safety certificates such as HACCP, GMP, ISO22000, etc., when registering the foreign food facilities. This new scheme aims to intensify the safety control of imported foods throughout the entire manufacturing procedure.
1. Imported foods whose facility needs to be differentially registered
Overseas facilities of health functional food are firstly designated to follow the new registration scheme. The trial period will be from April 1 to October 31, 2023. The authority plans to compulsorily implement the differential registration to facilities of health functional food facility in 2024, and to facilities of processed agricultural food and seasoning foods in 2025.
2. Scope of allowable certificates
MFDS introduced 7 kinds of safety certificates in the guideline2 of differential registration for foreign food facility. The scope of allowable certificates covers ISO 22000, HACCP, GMP, FSSC 22000, BRC Food, SQF, and IFS Food.
2.1 ISO 22000
Name | ISO 22000 | Mark |
|
Organization | ISO (International Organization for Standardization) | ||
Period of validity | 3 years | ||
Website | www.iso.org |
ISO 22000 adopts all 7 principles and 12 procedures of HACCP based on ISO 9001 (Quality Management System) to ensure food safety throughout the food supply chain. ISO 22000 sets out the requirements for a food safety management system. Enterprises intending to obtain the ISO 22000 certificate shall apply with ISO and have the facility certified to ISO requirements.
Examples of ISO 22000 certifications:

India China Italy Thailand
2.2 HACCP
Name | HACCP CERTIFICATE | Mark | Depending on the regulation in each country |
Organization | Depending on the regulation in each country | ||
Period of validity | Depending on the regulation in each country |
Hazard Analysis Critical Control Points (HACCP) ensures food safety by identifying and evaluating the hazards in the processes of food manufacturing, processing, cooking, portioning, and distribution to prevent the mixing of hazardous substances and/or contamination into foods.
HACCP is mandatory for fishery foods, canned foods, and some other specific foods in some country. In China, HACCP is conducted by organizations designated by Certification and Accreditation Administration of China (CNCA). There are also countries adopting HACCP as a voluntary certificate.
Examples of HACCP certifications:

China Vietnam Italy Paraguay
2.3 GMP
Name | GMP certificate | Mark | Depending on the regulation in each country |
Organization | Depending on the regulation in each country | ||
Period of validity | Depending on the regulation in each country |
Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) is a certification that ensures the safety and efficacy of food and drugs. In most countries, foods of specific categories such as health supplements are subject to GMP compulsorily. In the United States and Japan, food containing specified ingredients need to go through an inspection via private organizations.
Examples of HACCP certifications:

India the United States German Japan
2.4. FSSC
Name | FSSC 22000 Certificate | Mark |
|
Organization | Foundation for FSSC | ||
Period of validity | 3 years | ||
Website | www.fssc22000.com |
The FSSC (Food Safety System Certification) 22000 scheme contains a complete certification scheme for food safety management systems, using international and independent standards such as ISO 22000, ISO 9001, ISO/TS 22003, and technical specifications for sector-specific Pre-Requisite Programs (PRPs), including ISO/TS 22002-1.
Examples of FSSC 22000 certifications:
 Argentina Turkey England Japan
Argentina Turkey England Japan
2.5 BRC Food
Name | BRCGS (previously known as BRC) | Mark |
|
Organization | BRCGS | ||
Period of validity | 6 months/ 12 months | ||
Website | www.brcgs.com |
BRC Food, or BRC GS (Global Standards), refer to global standard food safety certifications for food safety, packaging materials, storage and distribution, consumer products, retail, gluten-free, plant-based and ethical trade, and more. The certifications are issued through the authorities approved by BRCGS in each country.
Examples of BRC Food certifications:

Vietnam Italy Thailand
2.6 SQF
Name | Safety quality food | Mark |
|
Organization | SQFI | ||
Period of validity | 6 months/ 12months | ||
Website | www.sqfi.com |
Safe Quality Food (SQF) certifies the food quality risk and food safety management with a focus on HACCP. Enterprises can obtain the SQF certification through a certification body that is accredited to the international standard ISO/IEC 17065:2012 and recognized by the Safe Quality Food Institute.
Examples of SQF certifications:

The United States Australia
2.7 IFS Food
Name | IFS certificate | Mark |
|
Organization | IFS | ||
Period of validity | 1 year | ||
Website | www.ifs-certification.com |
The IFS (International Featured Standards) Food Standard reviews the products and production processes to evaluate food producer’s ability to produce safe, authentic, and high-quality products according to legal requirements and customer specifications.
Examples of IFS Food certifications:

Portugal Swiss Italy India
3. Certification Submission Methods
Enterprises whose products are subject to the differential registration scheme can submit the safety certificates via MFDS imported food portal (https://impfood.mfds.go.kr) following the below steps:
(1) After logging in the website, applicant can click “전자민원(online service)” and “전자민원 바로가기(go to online service)” to access the registration webpage. 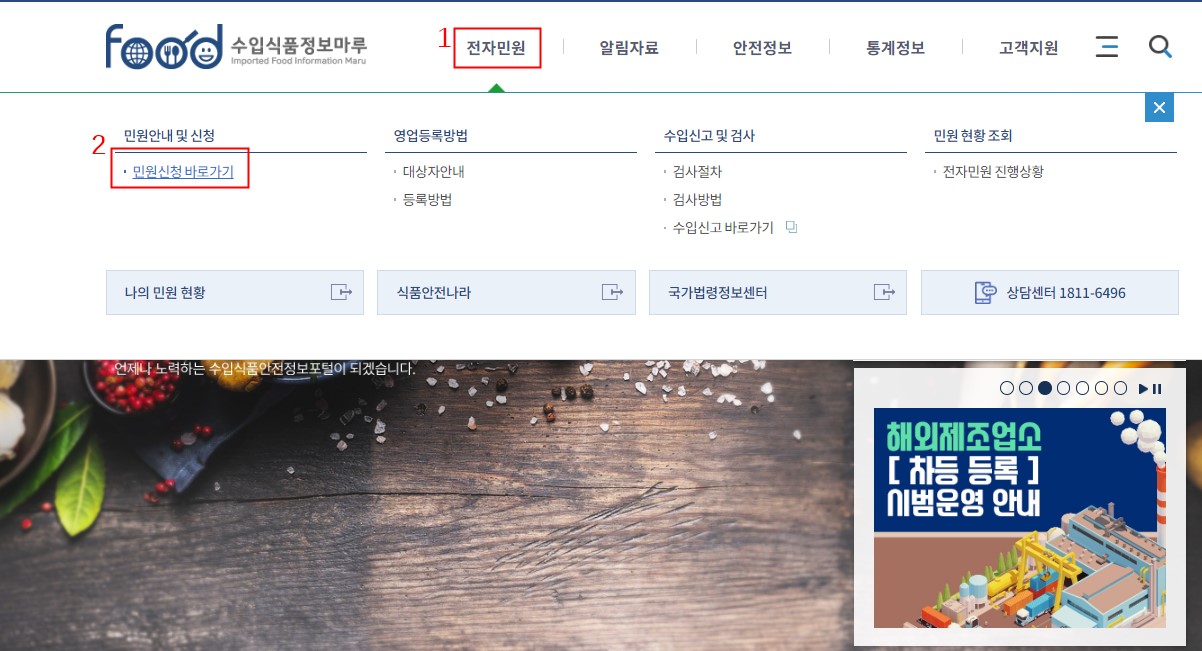
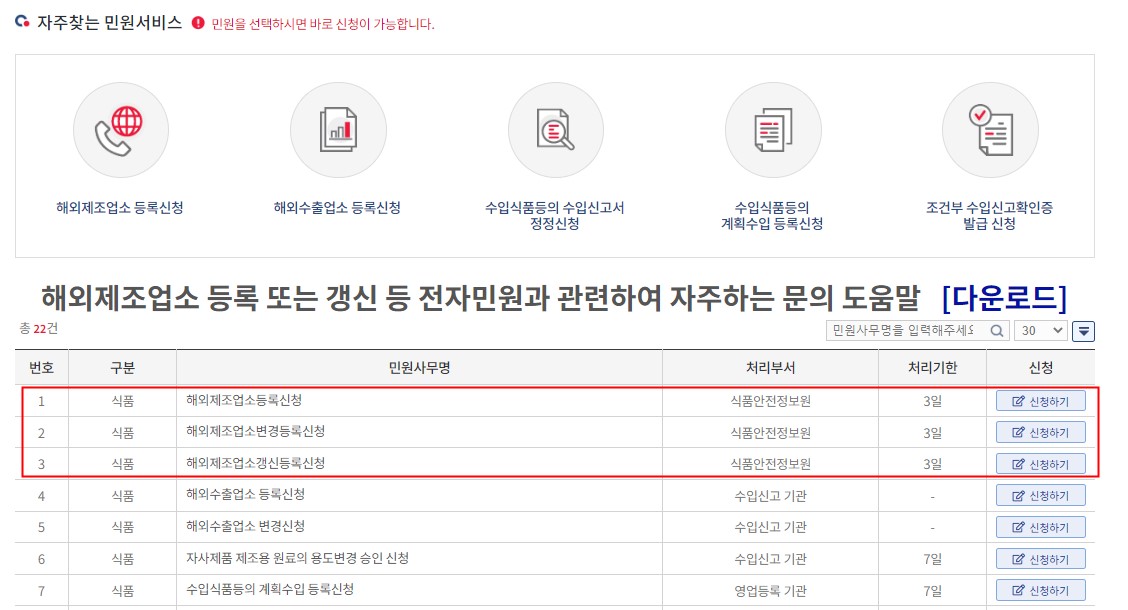
(2) Select the corresponding registration type to submit the certificate.
For un-registered facilities, choose “해외제조업등록신청(No. 1) (Application for registration of the foreign food facility)”. For registered facilities, choose “해외제조업변경등록신청(No. 2) (Application for changing registration of the foreign food facility)”. As for facilities whose registration expired applicant shall select “해외제조업갱신등록신청(No. 3) (Application for reviewing registration of the foreign food facility)”.
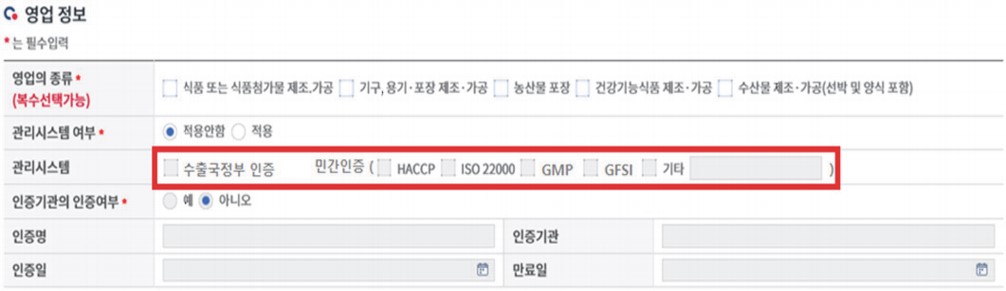
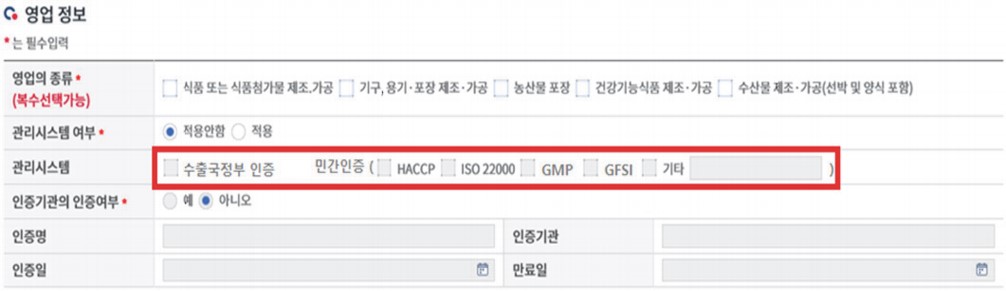
(3) The safety certificates are submitted via “영업정보 business information column”. Select the relevant certificate type and update the certificate file.
(4) The application result can be confirmed by entering the “전자민원 진행상황 (confirmation of application)” under the “전자민원(online service)”

4. Frequently Asked Questions
As published by MFDS in the guideline2, Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) cover the new scheme, certificate submission methods, and the answers are as the follows.
A. The pilot will start with high-risk health functional foods, and will gradually mandate additional items.
A. Products with potential risk were selected by weighting non-compliance records in the Customs and distribution steps, global risk information (physical, chemical, and biological), and import volume from 2017 to 2021.
Q3. During the pilot period, can I register my overseas facility without submitting a certificate?
A. During the pilot period, it is possible to register as an overseas manufacturer without submitting a certificate. However, it’s worth noting that the differential registration scheme will be mandatory after the pilot program in 2024. At that time, no submission of safety certificate will lead to the failure of foreign food facility registration for the specific imported food items.
A. Regardless of product type, import conditions, etc., all overseas manufacturers of health functional foods are subject to the risky food safety management and shall submit the safety certificate.
A. The authority accepts the submission of more than one safety certificates. However, submitting the certificate with the longest remaining period of validity is recommended.
A. For a register facility without submitting the safety certificate, it is recommend to submit a food safety management certificate when applying for the change or renewal of the foreign food facility registration.









 We provide full-scale global food market entry services (including product registration, ingredient review, regulatory consultation, customized training, market research, branding strategy). Please contact us to discuss how we can help you by
We provide full-scale global food market entry services (including product registration, ingredient review, regulatory consultation, customized training, market research, branding strategy). Please contact us to discuss how we can help you by 









