According to the violation cases of imported food announced by the Minister of Health, Labour and Welfare (MHLW), Japan rejected 733 batches of non-compliant foods from March 2021 to March 2022. Among them, 15% products failed because of unqualified food additives, involving exceeding limits or scope, failing to meet ingredient specifications, and using the additives that are not allowed to be used. This article interprets the Japanese additives regulation to help enterprises use additives compliantly and avoid access failures caused by improper use of additives.
Four Kinds of Food Additives in Japan
In Japan, the regulations on food additives have been continuously developing through long-term practice. Now the management on food additives has been systematic. In principle, only additives that received the designation by MHLW (designated food additives) can be used based on Article 12 of Food Sanitation Act.
However, in addition to the designated additives, substances in the list of existing food additives, natural flavoring agents, ordinary foods used as food additives are also allowed to be used as food additives;
1. Designated food additives
Designated food additive refers to safe additives approved by MHLW. Natural products and synthetic chemical substances are also included in the target of the designation.
The number of designated food additives has gradually increased with the continuous approval by MHLW. The latest update was on January 15, 2021. Four additives were added into the List of Designated Food Additives, including Ammonium Hydrogen Sulfite Water, Chitin-glucan, Dipotassium DL-Tartrate and Polyvinylimidazole - polyvinylpyrrolidone copolymers. Currently, there are a total of 472 designated food additives.
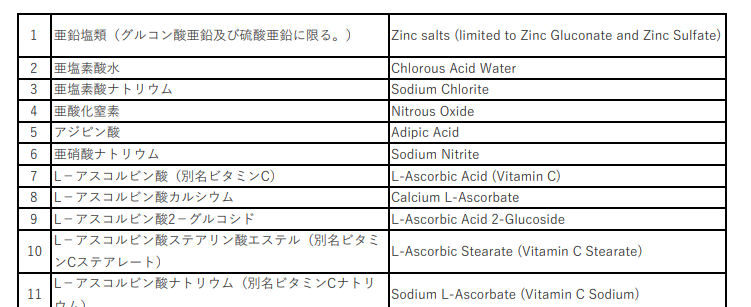
In addition, there are 18 kinds of additives noted by category name in the list, such as "ether kind(エーテル類)". These additives contain many kinds of non-toxic substances used as fragrances. Up to now, a total of 3,252 substances are in the list.
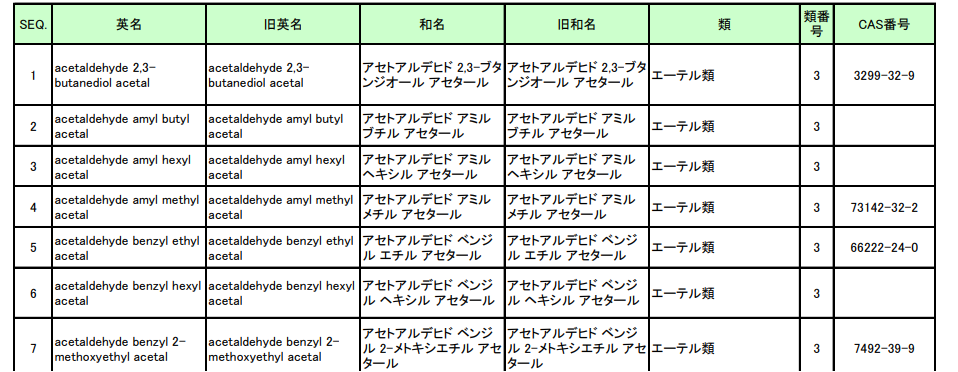
The latest news shows that although 3-acetyl-2,5-dimethylfuran (under the Keton kind) has little carcinogenic effect on human beings when used as a food additives, it proves to be a genotoxic carcinogen. Therefore, MHLW planned to delete this additive from December 31, 2022.
Notably, not all additives in the positive list have strict usage specifications. The MHLW formulates the allowable range, maximum limits and precautions for the use of food additives. However, some additives are only included in the positive list (List of Designated Food Additives), and there are no restrictions on the scope of application and dosage.
2. Existing food additives
Existing additive refers to safe natural additives widely used in Japan and has long-term consumption experience. According to the safety assessment, the List of Existing Food Additives will be dynamically updated. On February 26, 2020, nine kinds of existing additives were removed from the list, which is the latest change.

Because the existing food additives have been sold and used in the market for historical reasons, MHLW does not specify their use standards. However, there are exceptions for several individual existing food additives. For example, the limit requirement of Guaiac Resin as an antioxidant in Butter, Fats and oils is 1.0 g/kg.
3. Natural flavoring agents
Natural flavoring agents refer to natural products used for flavoring food that obtained from animals and plants or a mixture of the animals & plants, such as Vanilla and Crab. At present, there are 612 kinds of natural flavoring agents in Japan. The amount used in food is generally minimal.
4. Ordinary foods used as food additives
It refers to substances that can be both eaten or drunk directly as food and used as food additives.
These ordinary foods generally have four functions:
Thickeners: seaweed cellulose, kelp extract, etc.
Manufacturing agents: egg white, wheat flour, etc.
Bittering agents: hop extract, etc.
In addition, all additives must also meet the general standard for additive use and the specifications and storage standards for individual additives. You can find more specific requirements in ChemLinked's database via the links above.
What if you use an additive that is completely new to Japan?
If the product contains a significant additive and there is no suitable alternative, or the amount/object of the additive is different from the official requirements. In that case, enterprises can apply for a new designation or revision of food additives. Applicants need to submit additive information and safety data for evaluation. The standard period of this application process is one year, assuming that there is no need for supplementing incomplete materials.
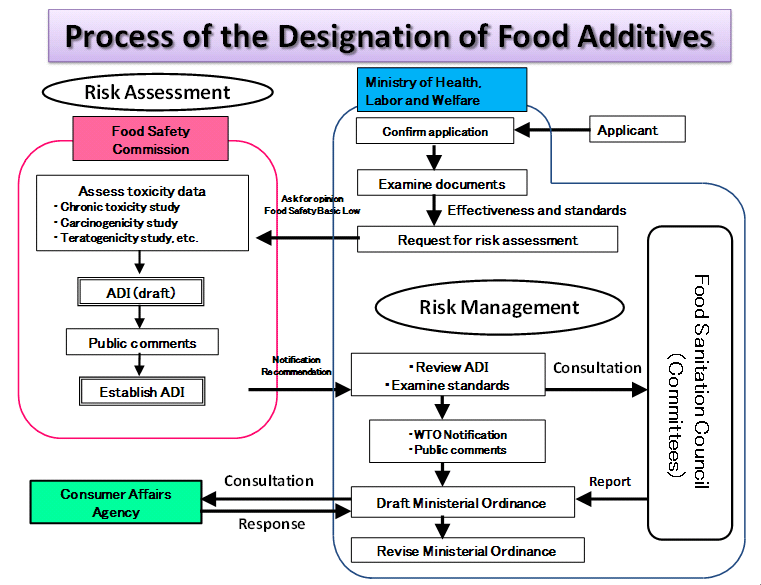
Documents required for application
Additive's basic information
1. Name and usage
2. Origin or process of discovery
3. Usage in other countries
5. Assessments by international organizations and other organizations
5. Physiochemical properties
6. Suggestions for usage standards
7. Others
Risk assessment
1. Tests for disposition in organisms
2. Toxicity
(1) Subchronic toxicity studies and chronic toxicity studies
(2) Carcinogenicity studies
(3) Toxicity/carcinogenicity combination studies with one-year repeated-dose administration
(4) Reproductive toxicity studies
(5) Prenatal developmental toxicity studies
(6) Genotoxicity studies
(7) Allergenic potential studies
(8) General pharmacological studies
(9) Other studies
3. Findings in humans
4. Estimation of daily intake, etc.
ChemLinked Suggestions
Whether a chemically synthesized substance or a natural substance, enterprises shall provide the ingredients’ standards, usage requirements, and safety data.
Keep an eye on the information of unqualified products released in Japan, and formulate corresponding preventive and control measures for the common risk types of products.
Whether it is a permitted additive? For example, unpermitted additives TBHQ and Cyclamate are often detected in imported products;
Whether it complies with the limited standard and applicable food scope? Sulfur dioxide is the most common additive used excessively;
Make sure the additives in the food comply with Japanese regulatory requirements before export. Japanese food additives are frequently updated. Exporting companies can get timely updates considering the language barrier by following ChemLinked platform.





 We provide full-scale global food market entry services (including product registration, ingredient review, regulatory consultation, customized training, market research, branding strategy). Please contact us to discuss how we can help you by
We provide full-scale global food market entry services (including product registration, ingredient review, regulatory consultation, customized training, market research, branding strategy). Please contact us to discuss how we can help you by 










